Segmented deformable mirrors¶
We will use segmented deformable mirrors and simulate the PSFs that result from segment pistons and tilts. We will compare this functionality against Poppy, another optical propagation package.
First we’ll import all packages.
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import astropy.units as u
import hcipy
import poppy
# Parameters - these will depend on the aperture function you use
PUP_DIAMETER = 0.019725 # m
GAPSIZE = 90e-6 # m
FLATTOFLAT = PUP_DIAMETER/7. # m
# these will not
num_pix = 1024
wavelength = 638e-9
num_airy = 20
sampling = 4
norm = False
Instantiate the segmented mirrors¶
HCIPy SM: hsm¶
We need to generate a pupil grid for the aperture, and a focal grid and propagator for the focal plane images after the DM.
# HCIPy grids and propagator
pupil_grid = hcipy.make_pupil_grid(dims=num_pix, diameter=PUP_DIAMETER)
focal_grid = hcipy.make_uniform_grid([2*num_airy*sampling]*2, 2*num_airy * wavelength / PUP_DIAMETER)
prop = hcipy.FraunhoferPropagator(pupil_grid, focal_grid)
We generate a segmented aperture for the segmented mirror. For convenience, we’ll use the HiCAT pupil without spiders. We’ll use supersampling to better resolve the segment gaps.
aper, segments = hcipy.make_hicat_aperture(normalized=norm, with_spiders=False, return_segments=True)
aper = hcipy.evaluate_supersampled(aper, pupil_grid, 1)
segments = hcipy.evaluate_supersampled(segments, pupil_grid, 1)
plt.title('HCIPy aperture')
hcipy.imshow_field(aper)
<matplotlib.image.NonUniformImage at 0x1bb45321f08>

Now we make the segmented mirror. In order to be able to apply the SM to
a plane, that plane needs to be a Wavefront, which combines a
Field - here the aperture - with a wavelength, here wavelength.
In this example here, since the SM doesn’t have any extra effects on the pupil since it’s completely flat still, we don’t actually have to apply the SM, although of course we could.
# Instantiate the segmented mirror
hsm = hcipy.SegmentedDeformableMirror(segments)
# Make a pupil plane wavefront from aperture
wf = hcipy.Wavefront(aper, wavelength)
# Apply SM if you want to
wf = hsm(wf)
plt.title('Wavefront intensity at HCIPy SM')
hcipy.imshow_field(wf.intensity)
<matplotlib.image.NonUniformImage at 0x1bb4602e088>

Poppy SM: psm¶
We’ll do the same for Poppy.
psm = poppy.dms.HexSegmentedDeformableMirror(name='Poppy SM',
rings=3,
flattoflat=FLATTOFLAT*u.m,
gap=GAPSIZE*u.m,
center=False)
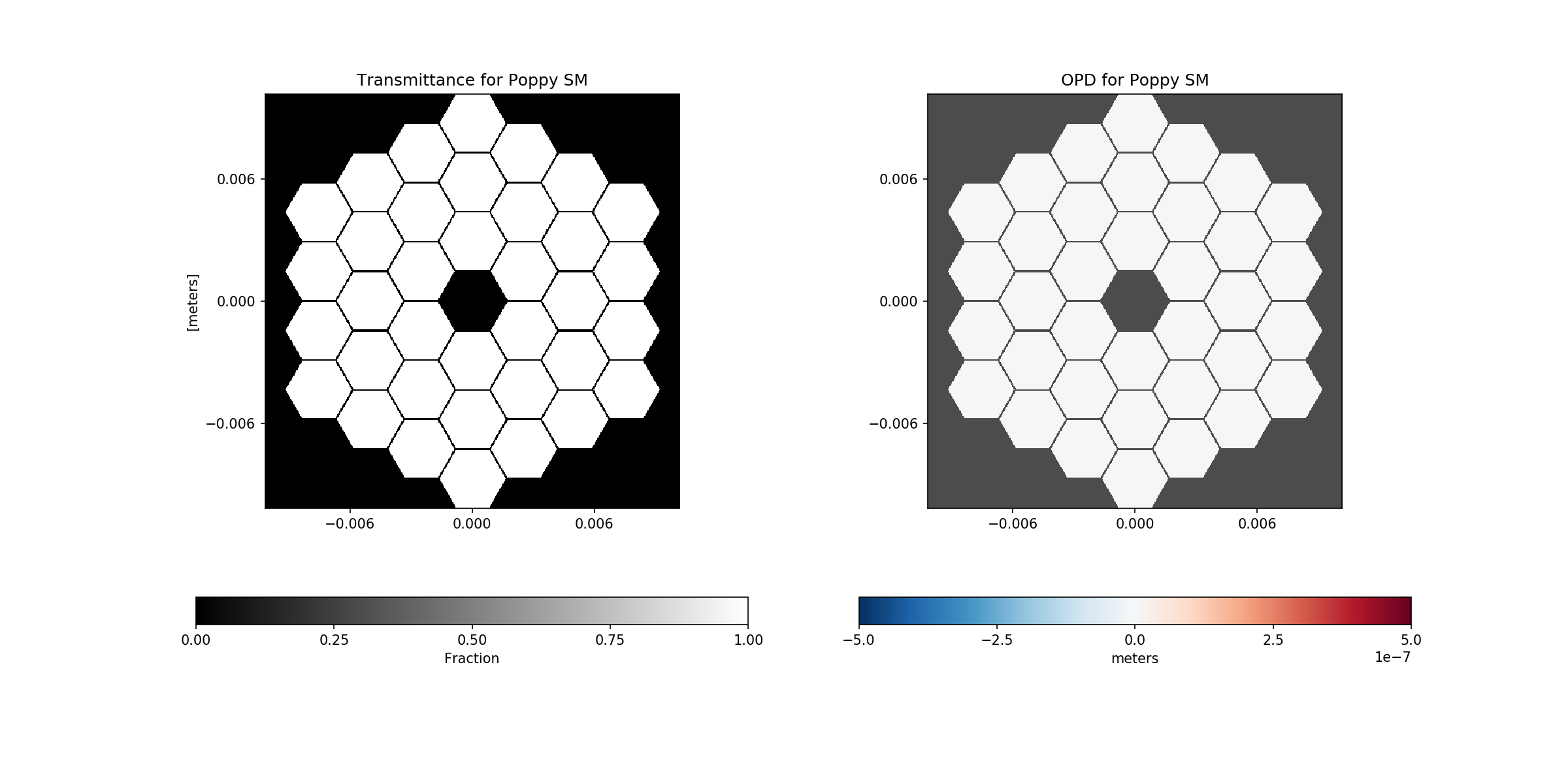
# Display the transmission and phase of the poppy sm
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 8))
psm.display(what='both')
(<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x1bb47083648>,
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x1bb474fc248>)
Create reference images¶
HCIPy reference image¶
We need to apply the SM to the wavefront in the pupil plane and then propagate it to the image plane.
# Apply SM to pupil plane wf
wf_sm = hsm(wf)
# Propagate from SM to image plane
im_ref_hc = prop(wf_sm)
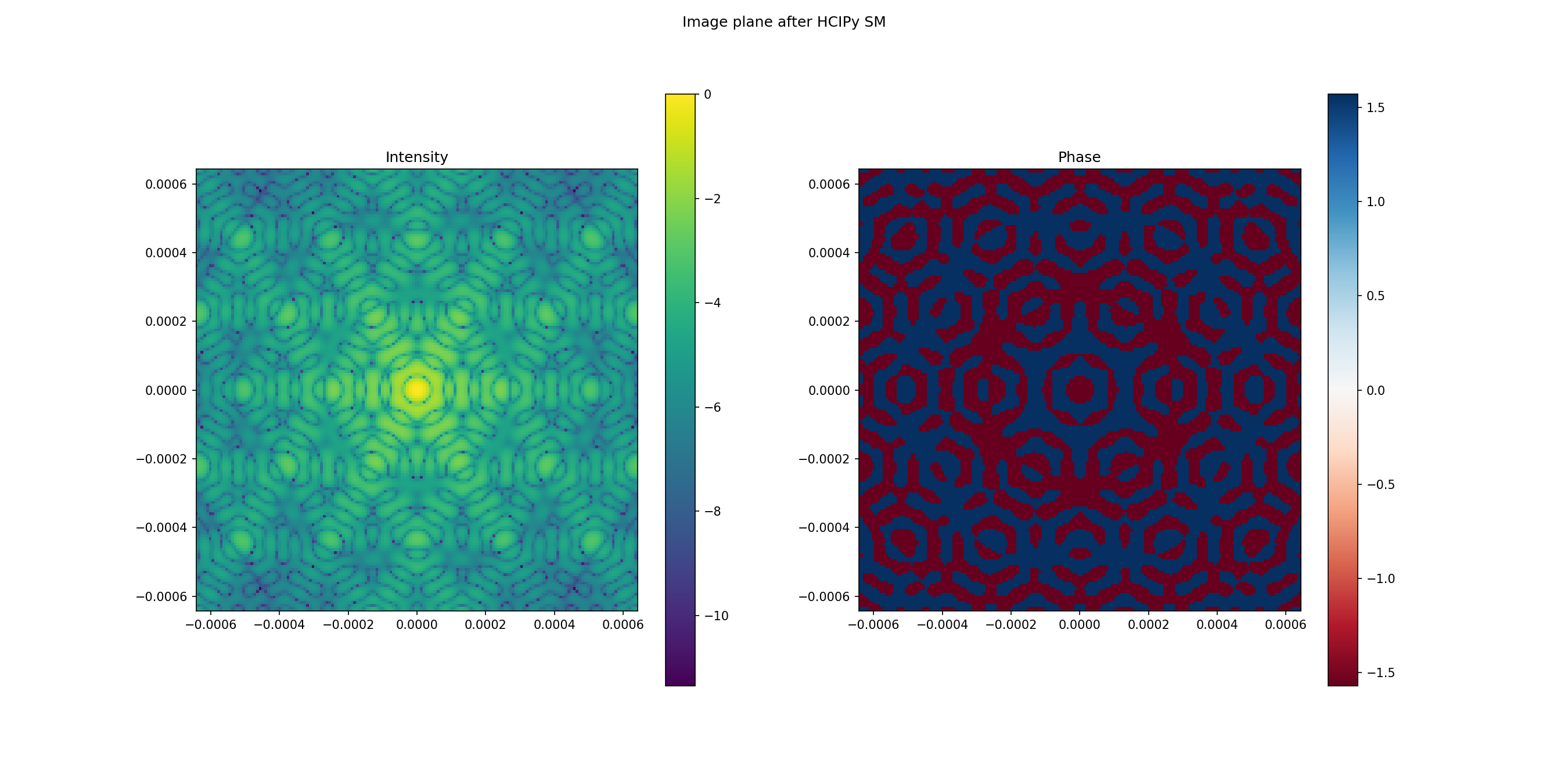
# Display intensity and phase in image plane
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 9))
plt.suptitle('Image plane after HCIPy SM')
# Get normalization factor for HCIPy reference image
norm_hc = np.max(im_ref_hc.intensity)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
hcipy.imshow_field(np.log10(im_ref_hc.intensity/norm_hc))
plt.title('Intensity')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
hcipy.imshow_field(im_ref_hc.phase, cmap='RdBu')
plt.title('Phase')
plt.colorbar()
print('HCIPy PSF shape: {}'.format(im_ref_hc.intensity.shaped.shape))
HCIPy PSF shape: (160, 160)
Poppy reference image¶
For the Poppy propagation, we need to make an optical system of which we then calculate the PSF.
I will try to match the image resolution and size of the HCIPy image. I
first adjust the pixelscale and fov_arcsec such that their ratio
works and then I add a tweak factor fac to scale it to the HCIPy
image. I also set oversample to something that matches the HCIPy
sampling (it’s close enough). I keep reusing these numbers and the tweak
factor later on in the notebook.
# Make an optical system with the Poppy SM and a detector
psm.flatten()
osys = poppy.OpticalSystem()
osys.add_pupil(psm)
fac = 5300
pxscle = 10 * np.degrees(wavelength / PUP_DIAMETER) * 3600.0 / sampling * 0.97
fovarc = pxscle * 160 / 10
osys.add_detector(pixelscale=pxscle, fov_arcsec=fovarc, oversample=10)
<poppy.poppy_core.Detector at 0x1bb48481d88>
# Calculate the PSF
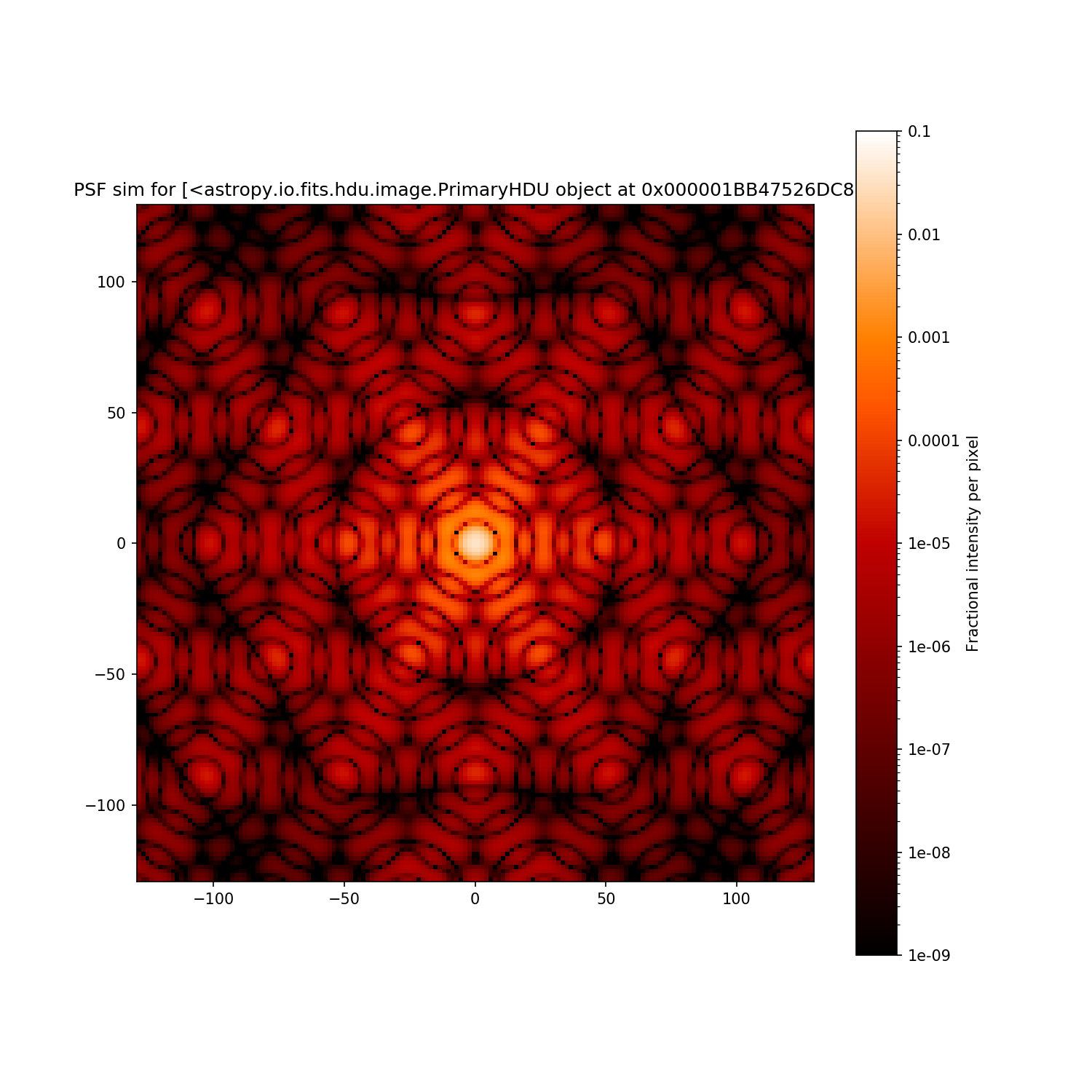
psf = osys.calc_psf(wavelength)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
poppy.display_psf(psf, vmin=1e-9, vmax=0.1)
# Get the PSF as an array
im_ref_pop = psf[0].data
print('Poppy PSF shape: {}'.format(im_ref_pop.shape))
# Get normalization from Poppy reference image
norm_pop = np.max(im_ref_pop)
Poppy PSF shape: (160, 160)
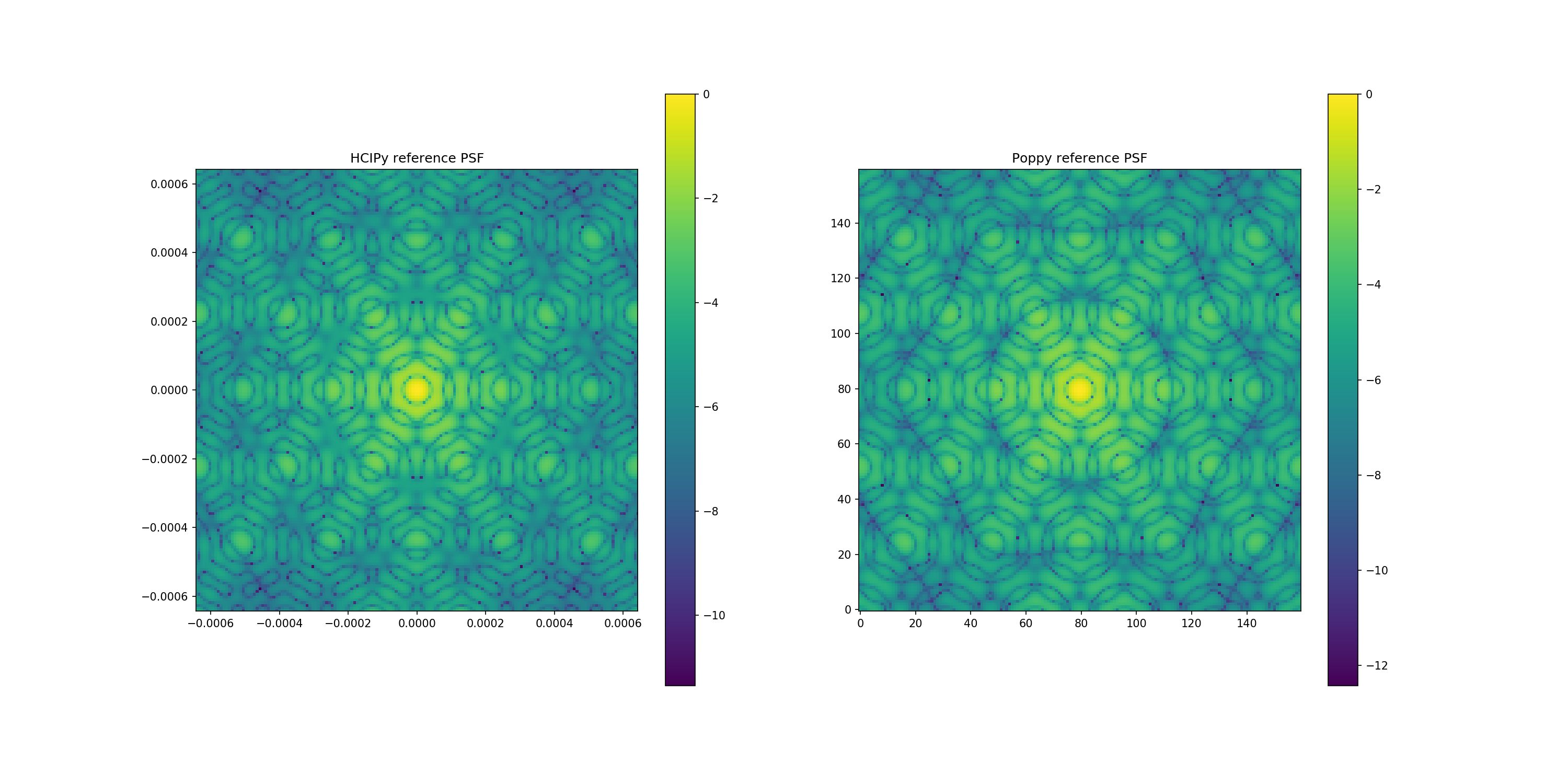
Both reference images side-by-side¶
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
hcipy.imshow_field(np.log10(im_ref_hc.intensity / norm_hc))
plt.title('HCIPy reference PSF')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.log10(im_ref_pop / norm_pop), origin='lower')
plt.title('Poppy reference PSF')
plt.colorbar()
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x1bb4834fa88>
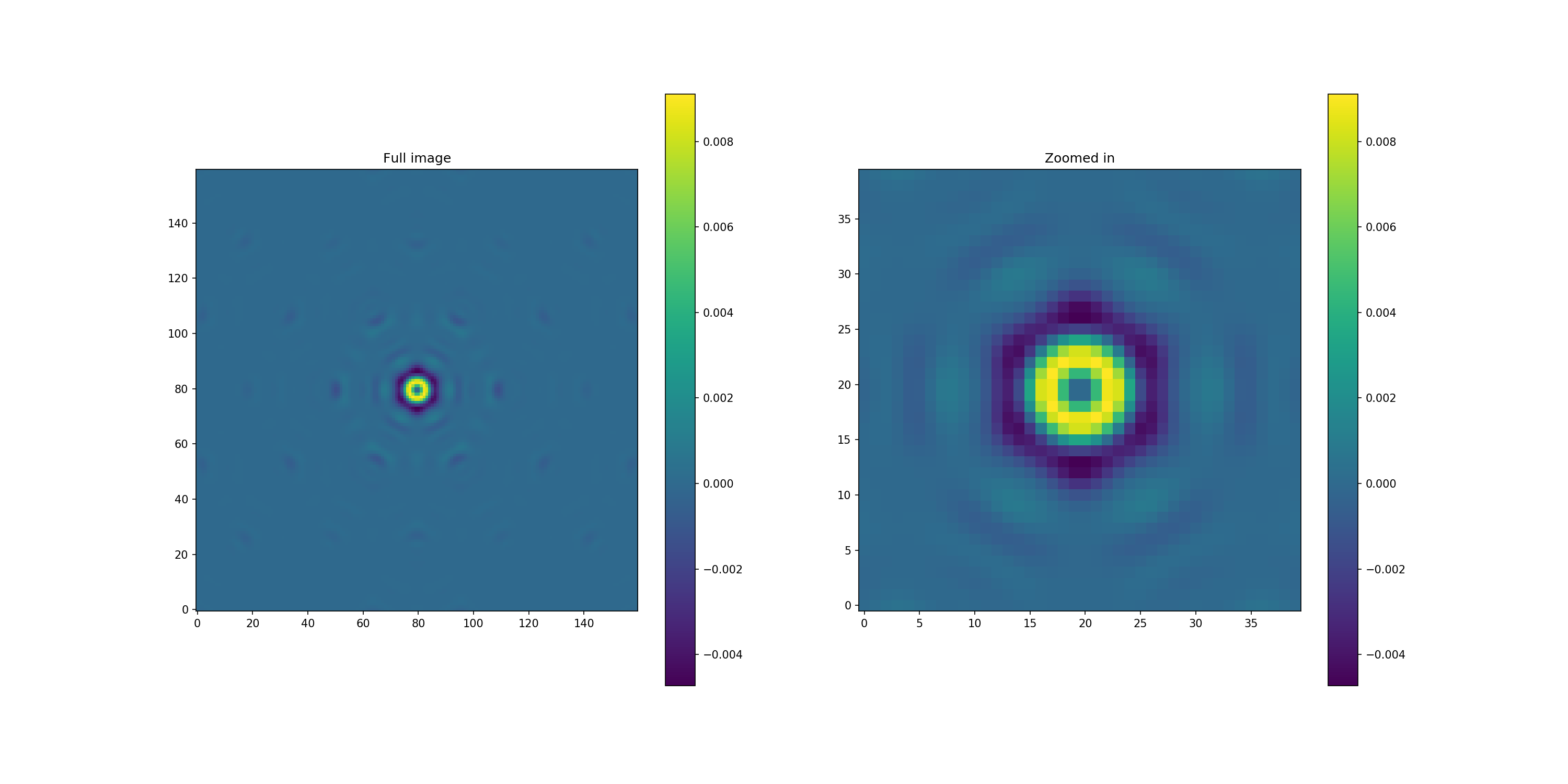
ref_dif = im_ref_pop / norm_pop - im_ref_hc.intensity.shaped / norm_hc
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(ref_dif, origin='lower')
plt.title('Full image')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(ref_dif[60:100,60:100], origin='lower')
plt.title('Zoomed in')
plt.colorbar()
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x1bb48475a48>
Applying aberrations¶
# Define function from rad of phase to m OPD
def aber_to_opd(aber_rad, wavelength):
aber_m = aber_rad * wavelength / (2 * np.pi)
return aber_m
aber_rad = 4.0
print('Aberration: {} rad'.format(aber_rad))
print('Aberration: {} m'.format(aber_to_opd(aber_rad, wavelength)))
Aberration: 4.0 rad
Aberration: 4.061634147705169e-07 m
# Flatten both SMs just to be sure
hsm.flatten()
psm.flatten()
poppy_to_hcipy_index = {
1: 2, 2: 1, 3: 0, 4: 5, 5: 4, 6: 3,
7: 10, 8: 9, 9: 8, 10: 7, 11: 6, 12: 17, 13: 16, 14: 15, 15: 14, 16: 13, 17: 12, 18: 11,
19: 24, 20: 23, 21: 22, 22: 21, 23: 20, 24: 19, 25: 18,
26: 35, 27: 34, 28: 33, 29: 32, 30: 31, 31: 30, 32: 29, 33: 28, 34: 27, 35: 26, 36: 25}
for i in [35, 25]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], aber_to_opd(aber_rad, wavelength) / 2, 0, 0)
psm.set_actuator(i, aber_to_opd(aber_rad, wavelength) * u.m, 0, 0)
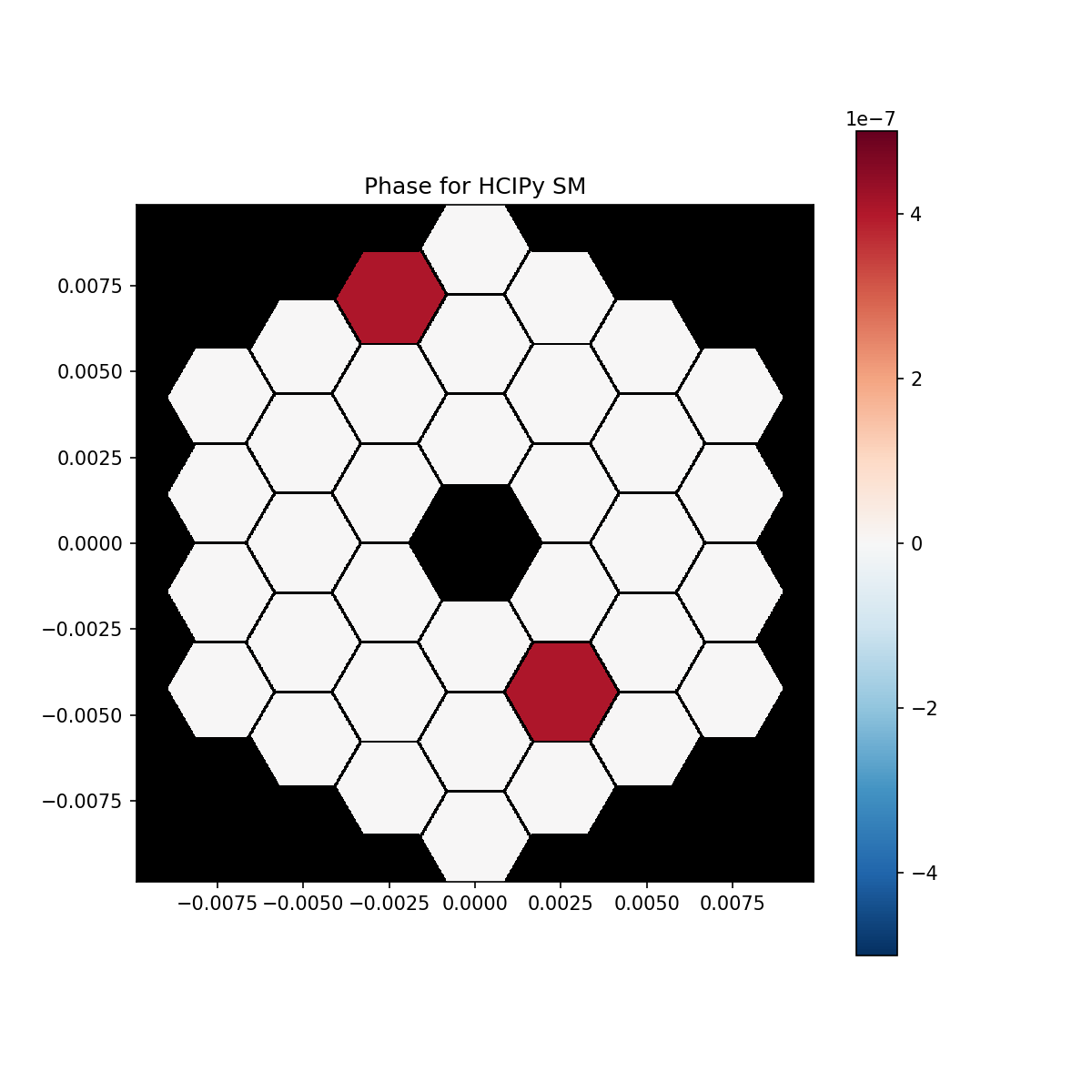
# Display both segmented mirrors in OPD
# HCIPy
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.title('Phase for HCIPy SM')
hcipy.imshow_field(hsm.surface * 2, mask=aper, cmap='RdBu_r', vmin=-5e-7, vmax=5e-7)
plt.colorbar()
# Poppy
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
psm.display(what='opd')
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x1bb47827548>

Show focal plane images¶
### HCIPy
# Apply SM to pupil plane wf
wf_fp_pistoned = hsm(wf)
# Propagate from SM to image plane
im_pistoned_hc = prop(wf_fp_pistoned)
### Poppy
# Make an optical system with the Poppy SM and a detector
osys = poppy.OpticalSystem()
osys.add_pupil(psm)
pxscle = 0.0031*fac # I'm tweaking pixelscale and fov_arcsec to match the HCIPy image
fovarc = 0.05*fac
osys.add_detector(pixelscale=pxscle, fov_arcsec=fovarc, oversample=10)
# Calculate the PSF
psf = osys.calc_psf(wavelength)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# Get the PSF as an array
im_pistoned_pop = psf[0].data
### Display intensity of both cases image plane
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 9))
plt.suptitle('Image plane after SM for $\phi$ = ' + str(aber_rad) + ' rad')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
hcipy.imshow_field(np.log10(im_pistoned_hc.intensity / norm_hc))
plt.title('HCIPy pistoned pair')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.log10(im_pistoned_pop / norm_pop), origin='lower')
plt.title('Poppy pistoned pair')
plt.colorbar()
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x1bb479e7e88>
<Figure size 1500x1500 with 0 Axes>
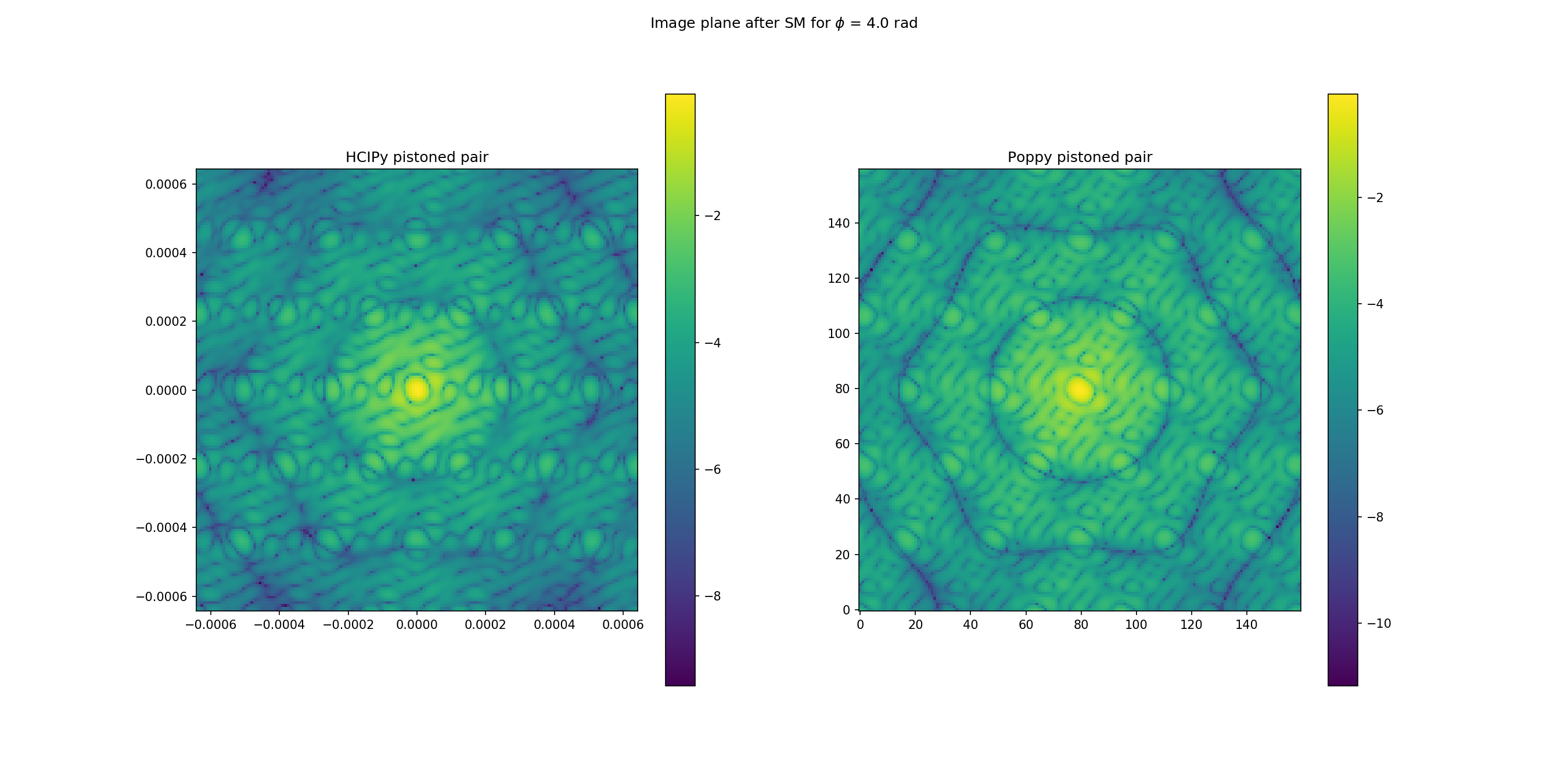
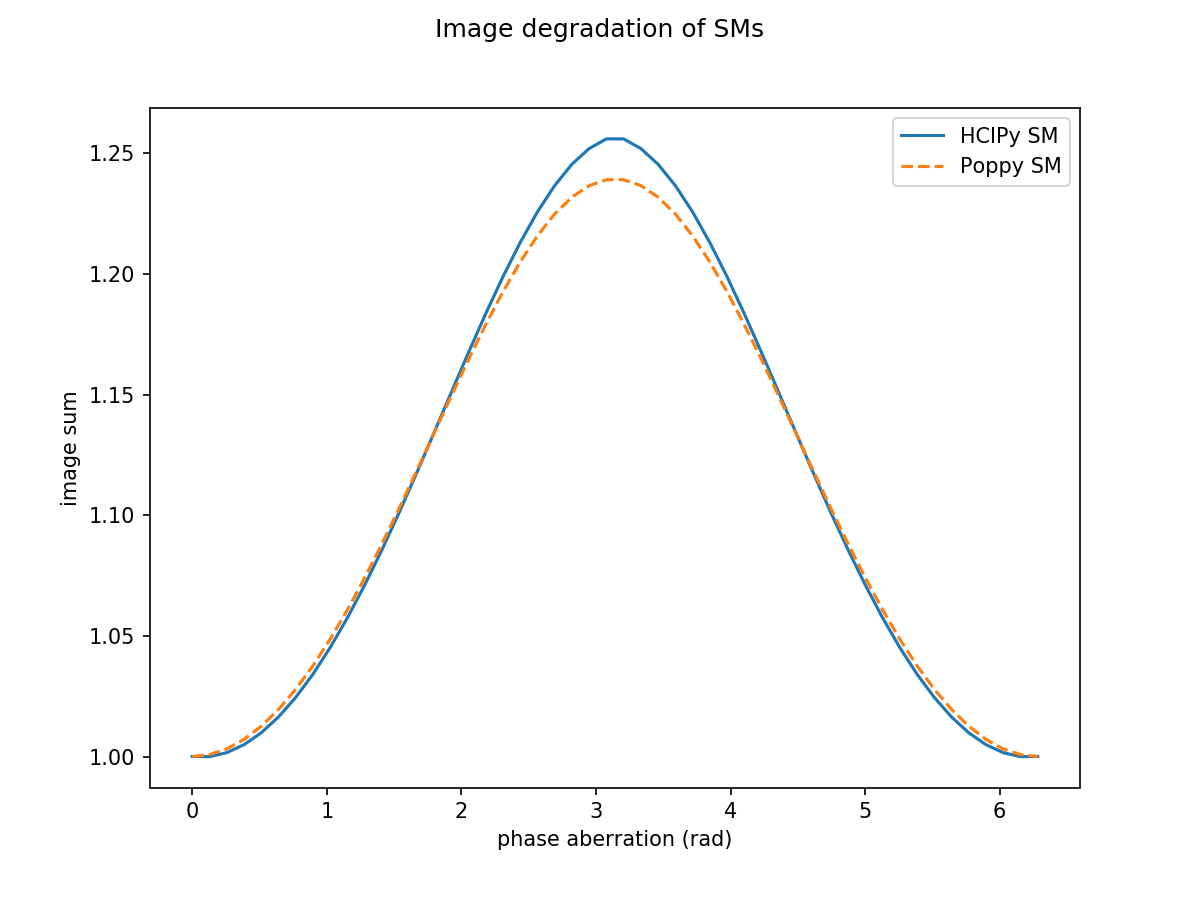
Image degradation as function of rms piston errors¶
We will plot the
# Aberration range
aber_array = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 50, True)
print('Aber in rad: \n{}'.format(aber_array))
print('Aber in m: \n{}'.format(aber_to_opd(aber_array, wavelength)))
# Apply pistons
hc_ims = []
pop_ims = []
for aber_rad in aber_array:
# Flatten both SMs
hsm.flatten()
psm.flatten()
# HCIPy
for i in [34, 25]:
opd = aber_to_opd(aber_rad, wavelength)
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], opd / 2, 0, 0) # hcipy uses SURFACE, not OPD
psm.set_actuator(i, opd * u.m, 0, 0)
# Propagate to image plane
# HCIPy:
# Propagate from pupil plane through SM to image plane
im_pistoned_hc = prop(hsm(wf))
# Poppy:
# Make an optical system with the Poppy SM and a detector
osys = poppy.OpticalSystem()
osys.add_pupil(psm)
pxscle = 0.0031 * fac # I'm tweaking pixelscale and fov_arcsec to match the HCIPy image
fovarc = 0.05 * fac
osys.add_detector(pixelscale=pxscle, fov_arcsec=fovarc, oversample=10)
# Calculate the PSF
psf = osys.calc_psf(wavelength)
# Get the PSF as an array
im_pistoned_pop = psf[0].data
hc_ims.append(im_pistoned_hc.intensity.shaped / im_pistoned_hc.intensity.max())
pop_ims.append(im_pistoned_pop / im_pistoned_pop.max())
hc_ims = np.array(hc_ims)
pop_ims = np.array(pop_ims)
Aber in rad:
[0. 0.12822827 0.25645654 0.38468481 0.51291309 0.64114136
0.76936963 0.8975979 1.02582617 1.15405444 1.28228272 1.41051099
1.53873926 1.66696753 1.7951958 1.92342407 2.05165235 2.17988062
2.30810889 2.43633716 2.56456543 2.6927937 2.82102197 2.94925025
3.07747852 3.20570679 3.33393506 3.46216333 3.5903916 3.71861988
3.84684815 3.97507642 4.10330469 4.23153296 4.35976123 4.48798951
4.61621778 4.74444605 4.87267432 5.00090259 5.12913086 5.25735913
5.38558741 5.51381568 5.64204395 5.77027222 5.89850049 6.02672876
6.15495704 6.28318531]
Aber in m:
[0.00000000e+00 1.30204082e-08 2.60408163e-08 3.90612245e-08
5.20816327e-08 6.51020408e-08 7.81224490e-08 9.11428571e-08
1.04163265e-07 1.17183673e-07 1.30204082e-07 1.43224490e-07
1.56244898e-07 1.69265306e-07 1.82285714e-07 1.95306122e-07
2.08326531e-07 2.21346939e-07 2.34367347e-07 2.47387755e-07
2.60408163e-07 2.73428571e-07 2.86448980e-07 2.99469388e-07
3.12489796e-07 3.25510204e-07 3.38530612e-07 3.51551020e-07
3.64571429e-07 3.77591837e-07 3.90612245e-07 4.03632653e-07
4.16653061e-07 4.29673469e-07 4.42693878e-07 4.55714286e-07
4.68734694e-07 4.81755102e-07 4.94775510e-07 5.07795918e-07
5.20816327e-07 5.33836735e-07 5.46857143e-07 5.59877551e-07
5.72897959e-07 5.85918367e-07 5.98938776e-07 6.11959184e-07
6.24979592e-07 6.38000000e-07]
### Quantify with image sums
sum_hc = np.sum(hc_ims, axis=(1,2))
sum_hc /= sum_hc[0]
sum_pop = np.sum(pop_ims, axis=(1,2))
sum_pop /= sum_pop[0]
plt.suptitle('Image degradation of SMs')
plt.plot(aber_array, sum_hc, '-', label='HCIPy SM')
plt.plot(aber_array, sum_pop, '--', label='Poppy SM')
plt.xlabel('phase aberration (rad)')
plt.ylabel('image sum')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
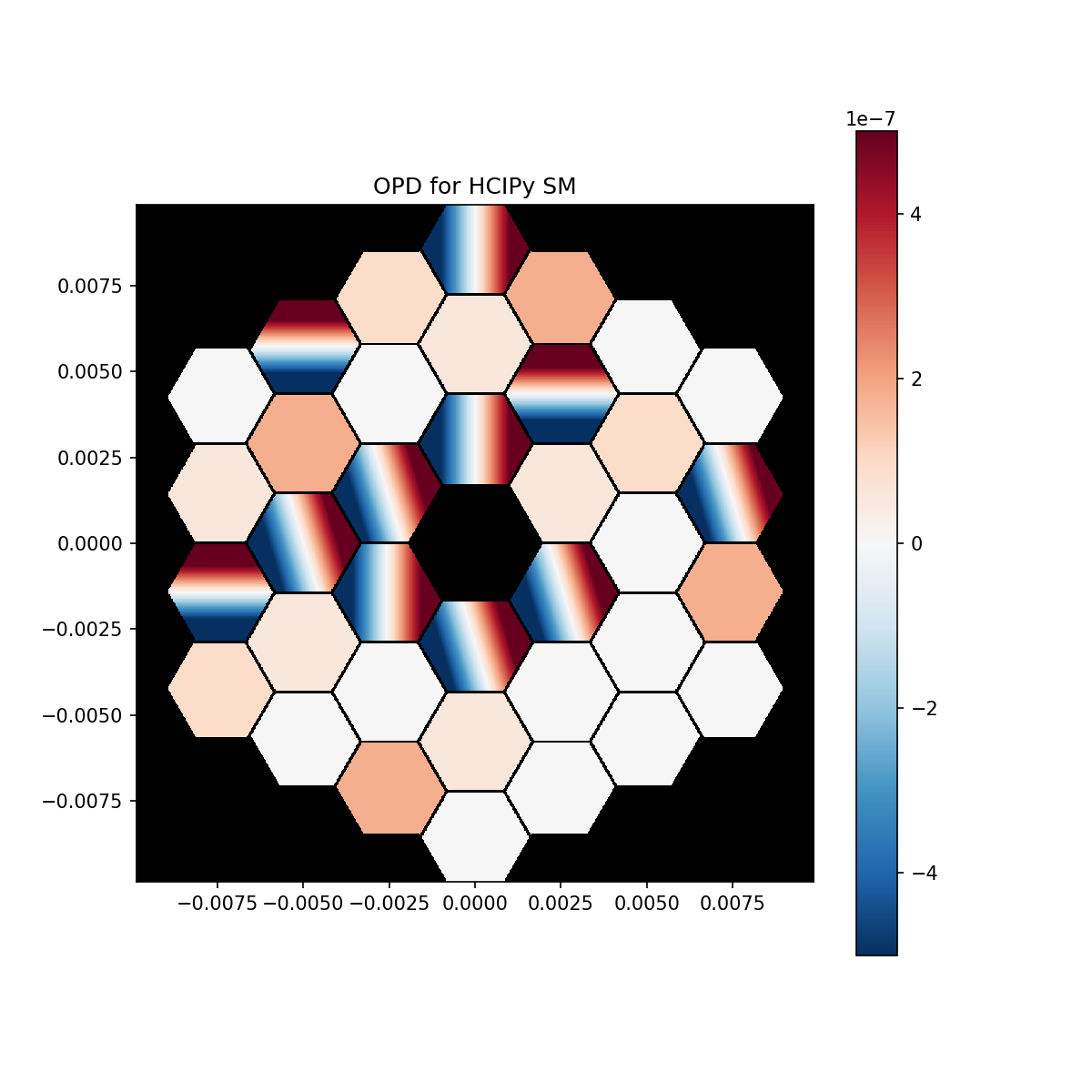
A mix of piston, tip and tilt (PTT)¶
aber_rad_tt = 500e-6
aber_rad_p = 1.8
opd_piston = aber_to_opd(aber_rad_p, wavelength)
### Put aberrations on both SMs
# Flatten both SMs
hsm.flatten()
psm.flatten()
## PISTON
for i in [19, 28, 23, 16]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], opd_piston / 2, 0, 0)
psm.set_actuator(i, opd_piston * u.m, 0, 0)
for i in [3, 35, 30, 8]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], 0.5 * opd_piston / 2, 0, 0)
psm.set_actuator(i, 0.5 * opd_piston * u.m, 0, 0)
for i in [14, 18, 1, 32, 12]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], 0.3 * opd_piston / 2, 0, 0)
psm.set_actuator(i, 0.3 * opd_piston * u.m, 0, 0)
## TIP and TILT
for i in [2, 5, 11, 15, 22]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], 0, aber_rad_tt / 2, 0.3 * aber_rad_tt / 2)
psm.set_actuator(i, 0, aber_rad_tt, 0.3 * aber_rad_tt)
for i in [4, 6, 36]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], 0, aber_rad_tt / 2, 0)
psm.set_actuator(i, 0, aber_rad_tt, 0)
for i in [34, 31, 7]:
hsm.set_segment_actuators(poppy_to_hcipy_index[i], 0, 0, 1.3 * aber_rad_tt / 2)
psm.set_actuator(i, 0, 0, 1.3 * aber_rad_tt)
# Display both segmented mirrors in OPD
# HCIPy
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.title('OPD for HCIPy SM')
hcipy.imshow_field(hsm.surface * 2, mask=aper, cmap='RdBu_r', vmin=-5e-7, vmax=5e-7)
plt.colorbar()
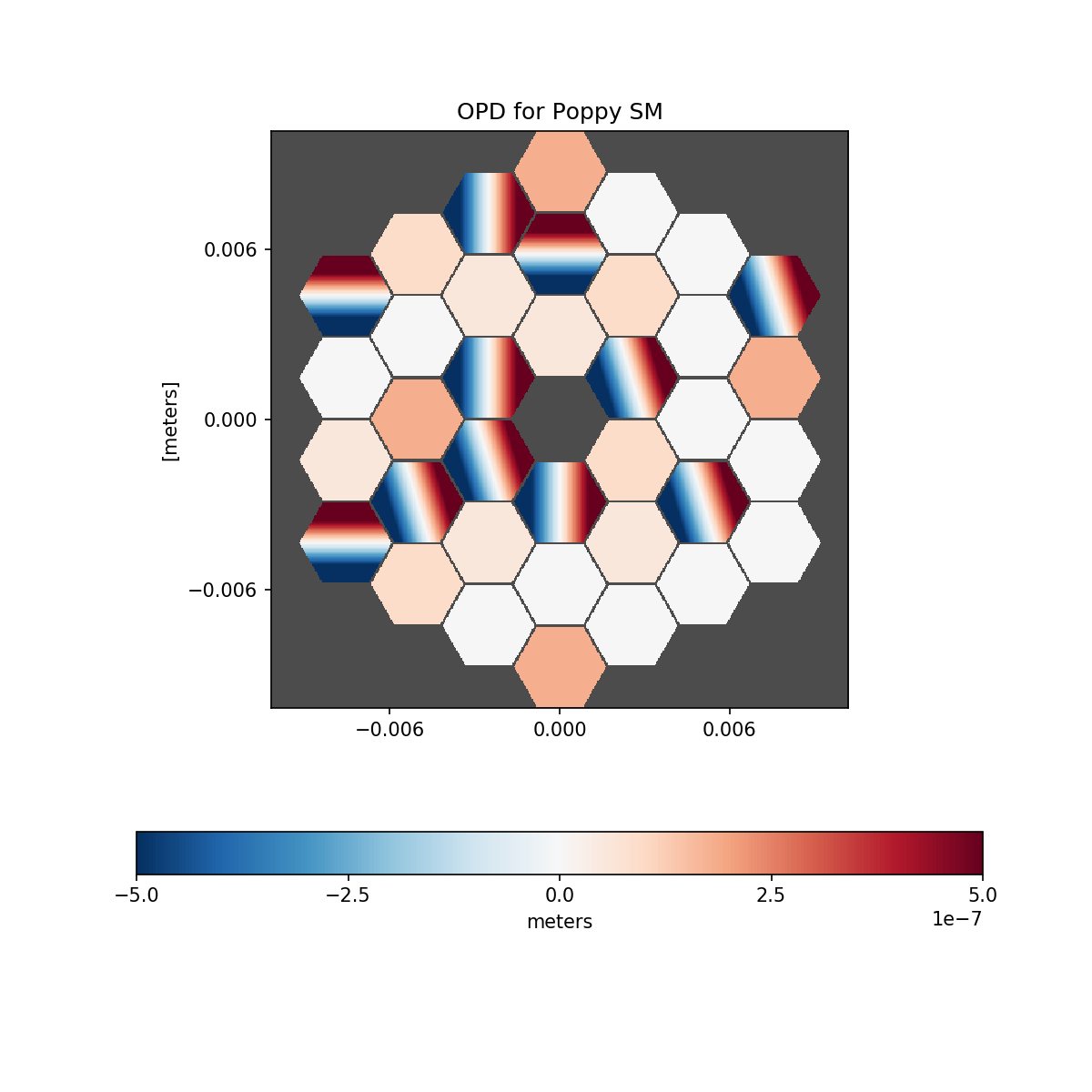
# Poppy
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
psm.display(what='opd')
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x1bb47de5508>
### Propagate to image plane
## HCIPy
# Propagate from pupil plane through SM to image plane
im_pistoned_hc = prop(hsm(wf))
## Poppy
# Make an optical system with the Poppy SM and a detector
osys = poppy.OpticalSystem()
osys.add_pupil(psm)
pxscle = 0.0031 * fac # I'm tweaking pixelscale and fov_arcsec to match the HCIPy image
fovarc = 0.05 * fac
osys.add_detector(pixelscale=pxscle, fov_arcsec=fovarc, oversample=10)
# Calculate the PSF
psf = osys.calc_psf(wavelength)
# Get the PSF as an array
im_pistoned_pop = psf[0].data
### Display intensity of both cases image plane
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 9))
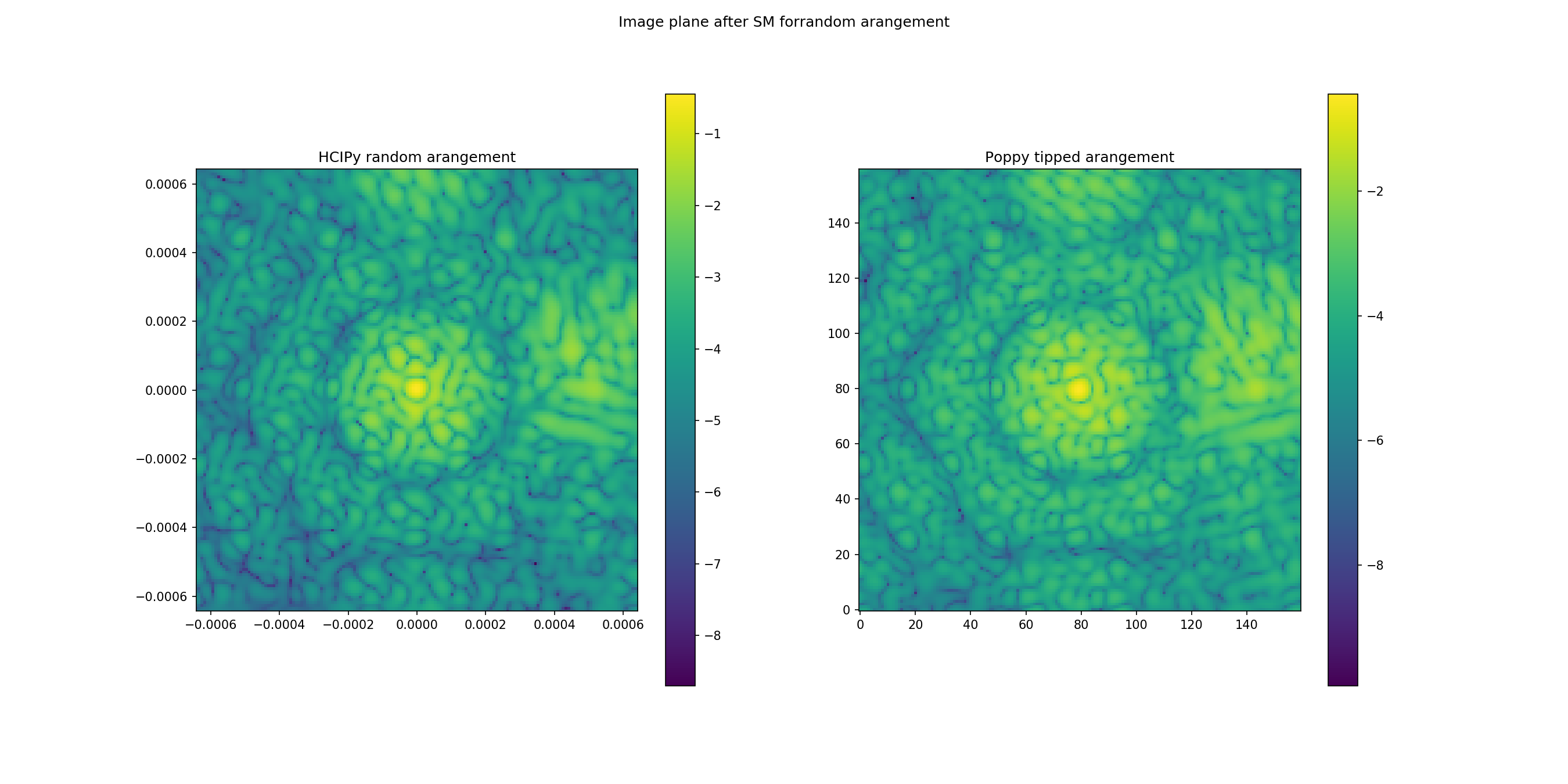
plt.suptitle('Image plane after SM forrandom arangement')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
hcipy.imshow_field(np.log10(im_pistoned_hc.intensity/norm_hc))
plt.title('HCIPy random arangement')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(np.log10(im_pistoned_pop/norm_pop), origin='lower')
plt.title('Poppy tipped arangement')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()